Omeros’ research technologies enable
Let science lead the way
Discovery Technologies
the discovery of next-generation
therapeutics to improve – and to
save – the lives of patients.
G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Deorphanization
We developed the first – and we believe the only – high-throughput system to identify synthetic ligands, including antagonists, agonists, and inverse agonists, that bind to and affect the function of orphan G protein-coupled receptors. This proprietary system has “unlocked” 54 orphan GPCRs to date. For comparison, in the same timeframe, the rest of the world collectively found synthetic ligands for only 4 orphan GPCRs.
Significance of GPCRs
GPCRs, which are cell surface membrane proteins involved in mediating both sensory and nonsensory functions, comprise one of the largest families of proteins in the genomes of multicellular organisms. The GPCR family represents an important source of drug discovery. GPCR-targeted drugs account for nearly 40% of all drugs sold worldwide.
Although GPCRs form a super-family of receptors, individual GPCRs display a high degree of specificity and affinity for the functionally active molecules, or ligands, that bind to a given receptor. When activated by its ligand, the GPCR interacts with intracellular G proteins, resulting in a cascade of signaling events inside the cell that ultimately leads to the particular function linked to the receptor. There are 370 non-sensory GPCRs with known ligands and 167 of them are drug targets – 108 for FDA approved medications and 66 for molecules in clinical trials.
Without a known ligand, there is no template for medicinal chemistry and no way to identify the GPCR’s signaling pathway. This means that drugs are very difficult to develop against orphan GPCRs. Only 7 of the 116 orphan GPCRs have had a drug developed against them. “Unlocking” an orphan GPCR by identifying one or more of its respective ligands can lead to the development of drugs that act at the previously undruggable receptor.
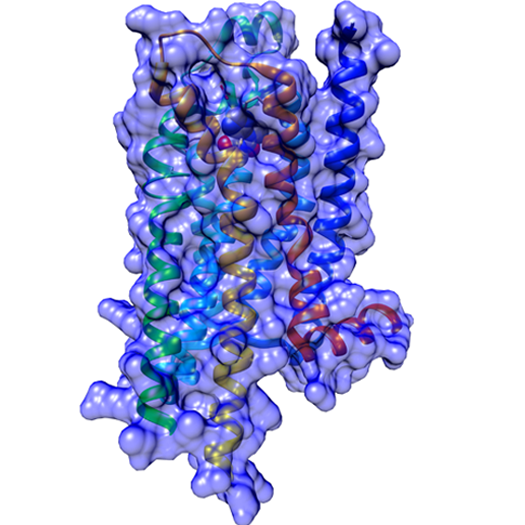

GPCR Deorphanization Technology
Omeros developed a proprietary cellular redistribution assay (CRA) that enables high-throughput identification of synthetic ligands, including antagonists, agonists and inverse agonists, that bind to and affect the function of orphan GPCRs. We believe that ours is the first and only assay capable of finding synthetic ligands for GPCRs in high throughput. Using our CRA, we have successfully identified and confirmed sets of compounds that interact selectively with the orphan receptors listed below.
GPCR Targets for Discovery
Omeros has identified and confirmed sets of compounds that interact selectively with the following orphan receptors:
| GPCR | Indication |
|---|---|
| GPR12 | Obesity, cognitive impairments |
| GPR21 | Obesity, diabetes |
| GPR22 | Cardiovascular diseases, anxiety |
| GPR25 | Arterial stiffness |
| GPR37L1 | Hypertension |
| GPR39 | Diabetes |
| GPR45 | Obesity |
| GPR50 | Metabolic disorders |
| GPR61 | Eating disorders |
| GPR82 | Appetite, body weight |
| GPR101 | Appetite, eating disorders |
| GPR132 | Atherosclerosis |
| GPR146 | Dyslipidemia, diabetes |
| GPR171 | Eating disorders |
| GPR176 | Atherosclerosis |
| SREB1/GPR27 | Diabetes |
| GPCR | Indication |
|---|---|
| GPR19 | Melanoma, lung cancer |
| GPR20 | Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, acute myeloid leukemia |
| GPR65 | Renal cell carcinoma, ovarian cancer, inflammation |
| GPR68 | Ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, osteoporosis |
| GPR80 | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| GPR87 | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| GPR150 | Ovarian cancer |
| GPR161 | Triple-negative breast cancer, sarcomas |
| GPR174 | Immuno-oncology |
| LGR4 | Cancer stem cells, bone diseases |
| LGR5 | Cancer stem cells, esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| P2Y8 | Leukemia lymphomas |
| GPCR | Indication |
|---|---|
| GPR17 | Myelin disorders, multiple sclerosis |
| GPR31 | Anxiety disorders |
| GPR37 | Parkinson’s disease |
| GPR52 | Schizophrenia |
| GPR63 | Autism |
| GPR78 | Bipolar disorder, schizophrenia |
| GPR139 | Motor disorders |
| GPR141 | Autism |
| GPR151 | Schizophrenia, cognitive impairments |
| GPR153 | Schizophrenia |
| MAS1 | Cognitive impairments |
| MRGE | Pain |
| OPN4 | Seasonal affective disorder, depression, jet lag, sleep disorders |
| SREB1/GPR27 | Schizophrenia |
| SREB2/GPR85 | Schizophrenia, obesity |
| SREB3/GPR173 | Schizophrenia, obesity |
| GPCR | Indication |
|---|---|
| GPR15 | Human immunodeficiency virus enteropathy, rheumatoid arthritis |
| GPR32 | Acute inflammatory responses |
| GPR83 | Autoimmune disease, post-traumatic stress disorder |
| GPR183 | Osteoporosis, Epstein-Barr virus infection |
| CCRL2 | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| LGR6 | Hair follicle stem cell dysfunction, wound healing |
| GPCR | Indication |
|---|---|
| GPR135 | |
| GPR162 | |
| GPR182 | |
| MRGF | |
| OPN5 |
Antibody Development
Our proprietary ex vivo platform for the discovery of novel, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies utilizes a chicken B-cell lymphoma cell line. Using our platform and other know-how and techniques, we have generated antibodies against several clinically significant targets, including highly potent antibodies against MASP-2, MASP-3 and MASP-1. We continue to add antibodies to our development pipeline against these and other important targets.
Related Pages

